The K to 12 Program covers Kindergarten and 12 years of basic education (six years of primary education, four years of Junior High School, and two years of Senior High School [SHS]) to provide sufficient time for mastery of concepts and skills, develop lifelong learners, and prepare graduates for tertiary education, middle-level skills development, employment, and entrepreneurship.

Every Filipino child now has access to early childhood education through Universal Kindergarten. At 5 years old, children start schooling and are given the means to slowly adjust to formal education.
Research shows that children who underwent Kindergarten have better completion rates than those who did not. Children who complete a standards-based Kindergarten program are better prepared, for primary education.
Education for children in the early years lays the foundation for lifelong learning and for the total development of a child. The early years of a human being, from 0 to 6 years, are the most critical period when the brain grows to at least 60-70 percent of adult size. [Ref: K to 12 Toolkit]
In Kindergarten, students learn the alphabet, numbers, shapes, and colors through games, songs, and dances, in their Mother Tongue.

Examples, activities, songs, poems, stories, and illustrations are based on local culture, history, and reality. This makes the lessons relevant to the learners and easy to understand.
Students acquire in-depth knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes through continuity and consistency across all levels and subjects.
Discussions on issues such as Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR), Climate Change Adaptation, and Information & Communication Technology (ICT) are included in the enhanced curriculum.
Students are able to learn best through their first language, their Mother Tongue (MT). Twelve (12) MT languages have been introduced for SY 2012-2013: Bahasa Sug, Bikol, Cebuano, Chabacano, Hiligaynon, Iloko, Kapampangan, Maguindanaoan, Meranao, Pangasinense, Tagalog, and Waray. Other local languages will be added in succeeding school years.
Aside from the Mother Tongue, English and Filipino are taught as subjects starting Grade 1, with a focus on oral fluency. In Grade 4, English and Filipino are used as the primary Medium of Instruction (MOI).
After Grade 1, every student can read in his or her Mother Tongue. Learning in Mother Tongue also serves as the foundation for students to learn Filipino and English easily.
Subjects are taught from the simplest concepts to more complicated concepts through grade levels in spiral progression. As early as elementary, students gain knowledge in areas such as Biology, Geometry, Earth Science, Chemistry, and Algebra.
For example, currently, in High School, Biology is taught in 2nd Year, Chemistry in 3rd Year, and Physics in 4th Year. In K to 12, these subjects are connected and integrated from Grades 7 to 10. This same method is used in other Learning Areas like Math.
Senior High School is two years of specialized upper secondary education; students may choose a career track based on aptitude, interests, and school capacity. The choice of career track will define the content of the subjects a student will take in Grades 11 and 12. These subjects fall under either the Core Curriculum or specific Career Pathways.
There are six subjects under the Core Curriculum. These are Humanities, Languages (English and/or Filipino), Math, Philosophy, Science, and Social Sciences. Current content from some General Education subjects is embedded in the SHS curriculum.
Each student in Senior High School can choose among five tracks: Business and Entrepreneurship; Humanities and Social Sciences; Science, Technology, and Engineering; Sports; and Technical-Vocational.
Students undergo On-the-Job Training (OJT) or immersion, which may include earn-while-you-learn opportunities, to provide them relevant exposure and actual experience in their chosen track.
TVET (Technical Vocational Education & Training) National Certificate. After finishing Grade 10, a student can obtain Certificates of Competency (COC) or a National Certificate Level I (NC I). After finishing a Technical-Vocational track in Grade 12, a student may obtain a National Certificate Level II (NC II), provided he/she passes the competency-based assessment of the Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA). NC I and NC II improve the employability of graduates in fields like Agriculture, Electronics, and Trade.
Modeling Best Practices for Senior High School. In SY 2012-2013, there are 30 public high schools and higher education institutions (HEIs) that have implemented Grade 11. This is a Research and Design (R&D) program to simulate different aspects of Senior High School in preparation for full nationwide implementation in SY 2016-2017. Modeling programs offered by these schools are based on students’ interests, community needs, and their respective capacities.
After going through Kindergarten, the enhanced Elementary and Junior High curriculum, and a specialized Senior High program, every K to 12 graduate will be ready to go into different paths – may it be further education, employment, or entrepreneurship. Every graduate will be equipped with:
- Information, media and technology skills,
- Learning and innovation skills,
- Effective communication skills, and
- Life and career skills.
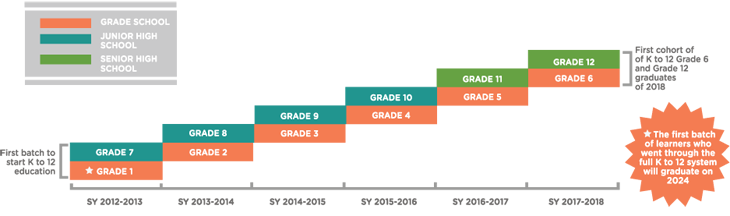
Program implementation in public schools is being done in phases starting SY 2012–2013. Grade 1 entrants in SY 2012–2013 are the first batch to fully undergo the program, and current 1st year Junior High School students (or Grade 7) are the first to undergo the enhanced secondary education program. To facilitate the transition from the existing 10-year basic education to 12 years, DepEd is also implementing the SHS and SHS Modeling.
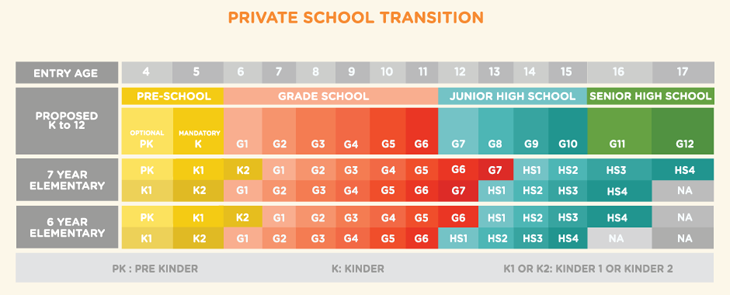
Private schools craft their transition plans based on (1) current/previous entry ages for Grade 1 and final year of Kinder, (2) duration of the program , and most importantly, (3) content of curriculum offered.